Using Data Visualization Tools takes center stage, offering a glimpse into a world where data comes alive through captivating visuals. Dive into the realm of charts, graphs, and dashboards that revolutionize the way we interpret information.
Explore the power of visual data representation and discover how these tools can transform complex data sets into clear, actionable insights for various industries and decision-making processes.
Introduction to Data Visualization Tools: Using Data Visualization Tools
Data visualization is the graphical representation of information and data. It uses visual elements like charts, graphs, and maps to help people understand the significance of data. By using visualization tools, complex data can be presented in an easier-to-understand format, making it more accessible and actionable.
Popular Data Visualization Tools
- Tableau: Known for its interactive dashboards and ease of use.
- Microsoft Power BI: Offers advanced analytics capabilities and seamless integration with Microsoft products.
- Google Data Studio: Free tool that enables users to create interactive reports and dashboards.
- D3.js: JavaScript library for producing dynamic and interactive data visualizations in web browsers.
Importance of Data Visualization Tools
Data visualization tools are crucial in various industries for making informed decisions, identifying trends, and communicating insights effectively. They help businesses in marketing, finance, healthcare, and more to gain a competitive edge by presenting complex data in a visually appealing manner.
Benefits of Visualizing Data
- Enhanced Data Understanding: Visual representations make it easier to interpret and analyze data quickly.
- Improved Decision Making: Visualizations help in spotting patterns and outliers that may not be apparent in raw data.
- Increased Engagement: Visuals capture attention and engage viewers more effectively than text-based information.
- Effective Communication: Visualizations simplify complex concepts and facilitate better communication of insights within teams and with stakeholders.
Types of Data Visualization Tools
Data visualization tools come in various categories, each with its unique features and functionalities. Let’s dive into the different types of data visualization tools:
Charts, Using Data Visualization Tools
Charts are one of the most common types of data visualization tools. They are visual representations of data, making it easier to identify patterns and trends. Some common types of charts include:
- Bar Charts: Used to compare different categories of data.
- Line Charts: Show trends over time.
- Pie Charts: Display parts of a whole.
Graphs
Graphs are another essential type of data visualization tool that focus on relationships between data points. Some common types of graphs include:
- Scatter Plots: Show the relationship between two variables.
- Network Graphs: Display connections between nodes.
- Heatmaps: Visualize data density in a matrix format.
Dashboards
Dashboards are comprehensive data visualization tools that provide an overview of key metrics and KPIs in one place. They often include multiple charts, graphs, and other visual elements to help users monitor performance and make informed decisions.
Each type of data visualization tool has its strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different data analysis needs. Charts are great for comparing data sets, graphs are useful for identifying relationships, and dashboards offer a holistic view of various metrics. By understanding the features and functionalities of each type of tool, users can choose the right one for their specific data analysis requirements.
Best Practices for Using Data Visualization Tools
When it comes to using data visualization tools, there are certain best practices that can help you make the most out of your data. From choosing the right tool to creating visually appealing visualizations, these practices can greatly enhance the effectiveness of your data analysis.
Choosing the Right Visualization Tool
- Start by understanding the type of data you have and the insights you want to gain from it. Different visualization tools are suited for different types of data, so it’s important to choose one that aligns with your specific needs.
- Consider the complexity of your data and the level of interactivity you require. Some tools offer more advanced features for complex data sets, while others are more user-friendly for simple visualizations.
- Take into account your team’s skill levels and familiarity with the tool. Opt for a tool that is easy to use and offers adequate support and training resources.
Creating Visually Appealing and Effective Data Visualizations
- Keep your visualizations simple and clutter-free. Avoid unnecessary elements that can distract from the main message you’re trying to convey.
- Use appropriate colors and fonts to enhance readability and make your visualizations more engaging. Stick to a consistent color scheme to maintain coherence across multiple charts or graphs.
- Include clear labels and titles to help viewers understand the data at a glance. Provide context and explanations where necessary to guide interpretation.
Interpreting and Communicating Insights from Visualized Data
- Focus on the key takeaways from your visualizations and use them to tell a compelling data-driven story. Highlight trends, patterns, and outliers that are relevant to your audience.
- Use annotations, callouts, and tooltips to provide additional context and details on specific data points. This can help viewers explore the data further and draw their own conclusions.
- Be prepared to answer questions and explain the insights derived from your visualizations. Practice effective data storytelling to ensure your audience grasps the significance of the data presented.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Data Visualization Tools
- Avoid using misleading visualizations that distort or exaggerate the data. Stick to accurate representations that reflect the true nature of the data.
- Avoid overcrowding your visualizations with unnecessary information or visual elements. Keep them focused on the key metrics and trends you want to highlight.
- Avoid relying solely on visualizations without providing context or explanations. Ensure that your audience understands the data and the insights you’re trying to convey.
Case Studies on Data Visualization
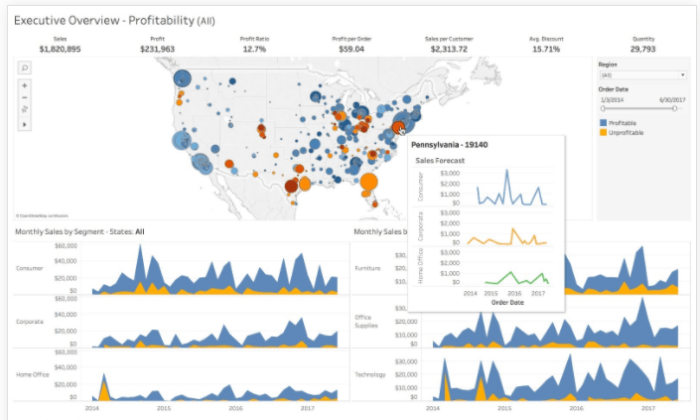
Data visualization tools have revolutionized the way organizations process and understand data. Let’s explore some real-world examples of how these tools have made a significant impact on decision-making processes and business operations.
Healthcare Industry
In the healthcare industry, organizations like Johns Hopkins Hospital have used data visualization tools to track and analyze patient data in real-time. By visualizing data on the spread of diseases or patient outcomes, healthcare providers can make informed decisions quickly. This has led to improved patient care and more efficient resource allocation.
Retail Sector
Companies like Amazon have leveraged data visualization tools to analyze customer behavior patterns and preferences. By visualizing data on shopping habits, product preferences, and market trends, Amazon can tailor their offerings to meet customer needs effectively. This has resulted in increased sales and customer satisfaction.
Finance and Banking
Financial institutions such as JP Morgan Chase have utilized data visualization tools to monitor market trends, analyze investment portfolios, and identify potential risks. By visualizing complex financial data, they can make better-informed decisions and mitigate risks effectively. This has helped them optimize their operations and improve profitability.
Challenges and Lessons Learned
Despite the numerous benefits of data visualization tools, organizations often face challenges in implementing these projects. Common challenges include data integration issues, ensuring data accuracy, and training employees to use the tools effectively. However, by overcoming these challenges, organizations can unlock the full potential of data visualization tools and drive innovation in their operations.