Blockchain technology sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Dive into the world of blockchain and discover its impact on various industries.
Overview of Blockchain Technology
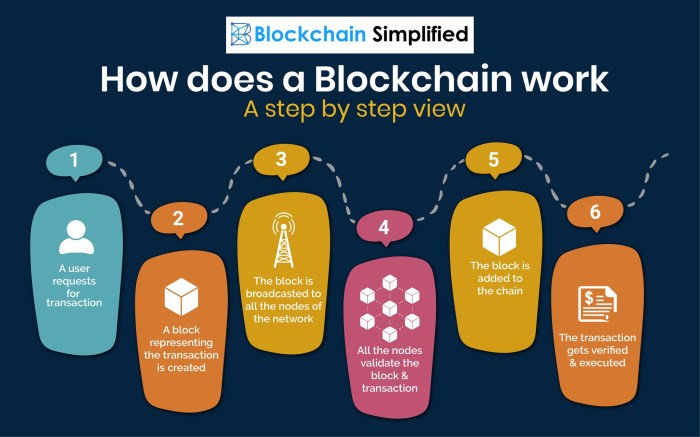
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed ledger system that allows data to be stored in a chain of blocks. Each block contains a list of transactions that are securely linked using cryptography. The decentralized nature of blockchain means that there is no central authority controlling the network, making it transparent and resistant to fraud.
Decentralization in Blockchain Technology
Decentralization in blockchain technology refers to the absence of a central authority governing the network. Instead, transactions are verified and recorded by a network of nodes spread across the globe. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of manipulation and ensuring trust among participants.
Role of Cryptography in Securing Blockchain Transactions
Cryptography plays a crucial role in securing blockchain transactions by encrypting the data stored in each block. This ensures that only authorized users can access and modify the information, maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of the transactions. Additionally, cryptographic techniques such as digital signatures are used to verify the identity of participants and authenticate transactions on the network.
Types of Blockchains
Blockchain technology can be categorized into different types based on their access, control, and governance. The two main types of blockchains are public and private blockchains. Public blockchains are open to anyone who wants to participate, allowing for transparency and decentralization. On the other hand, private blockchains restrict access to a specific group of users, making them more centralized and suitable for organizations with specific privacy requirements.
Permissioned and Permissionless Blockchains
Permissioned blockchains require users to have explicit permission to join the network and participate in transactions. This type of blockchain is often used in enterprise settings where privacy and control are essential. In contrast, permissionless blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open to anyone without the need for permission. These blockchains rely on consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the network.
Comparison of Blockchain Platforms
- Ethereum: Known for its smart contract functionality, Ethereum allows developers to create decentralized applications (dApps) on its platform. It uses the proof-of-work consensus mechanism but is in the process of transitioning to proof-of-stake to improve scalability and energy efficiency.
- Bitcoin: The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, Bitcoin operates on a public blockchain and uses proof-of-work to validate transactions. It is primarily used as a store of value and a medium of exchange.
- Hyperledger: Developed by the Linux Foundation, Hyperledger is a permissioned blockchain platform designed for enterprise use. It offers a range of tools and frameworks for businesses to build and deploy blockchain solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is not only revolutionizing the financial industry but also making a significant impact in various other sectors such as healthcare, supply chain, and real estate. The decentralized and secure nature of blockchain has paved the way for innovative solutions in these industries, ensuring transparency, efficiency, and trust among participants.
Finance
Blockchain is widely used in finance for secure and transparent transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have gained popularity as digital assets, enabling instant cross-border payments and reducing transaction costs.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, blockchain is utilized for securely storing patient records, ensuring data integrity, and sharing medical information across different healthcare providers. This technology enhances patient privacy, streamlines processes, and reduces medical errors.
Supply Chain
Blockchain is transforming the supply chain by providing a transparent and immutable ledger for tracking the movement of goods from manufacturer to consumer. Companies can trace the origin of products, verify authenticity, and ensure ethical sourcing practices, promoting trust and accountability.
Real Estate
Real estate transactions are being revolutionized by blockchain technology through smart contracts, which automate and secure property deals. Blockchain enables fractional ownership, eliminates the need for intermediaries, and reduces the risk of fraud in property transactions.
Cybersecurity and Data Integrity
Blockchain plays a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity by providing a tamper-proof mechanism for storing sensitive data. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that data cannot be altered retroactively, protecting against cyber threats and ensuring data integrity across various industries.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps)

Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute and enforce the terms of the agreement without the need for intermediaries, providing security and transparency in transactions.
Decentralized Applications (DApps) are applications that run on a decentralized network of computers rather than a single central server. They leverage blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer interactions without the need for intermediaries, ensuring decentralization and autonomy in operations.
Significance of Smart Contracts and DApps, Blockchain technology
Smart contracts and DApps play a crucial role in the blockchain ecosystem by streamlining processes, reducing costs, and increasing transparency. They eliminate the need for third-party intermediaries, offering security, efficiency, and trust in transactions.
- Smart contracts automate processes by executing predefined actions when specific conditions are met, reducing the risk of fraud and errors.
- DApps enable users to interact directly with each other, fostering a decentralized environment and promoting peer-to-peer transactions.
- Together, smart contracts and DApps revolutionize industries by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing security in various sectors such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more.
Smart contracts and DApps revolutionize industries by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing security in various sectors.
