Blockchain technology, the innovative backbone of the digital era, is reshaping the way we perceive security and transparency in transactions. From decentralized networks to smart contracts, let’s dive into the captivating realm of blockchain technology.
Overview of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers in a secure and transparent manner. The fundamental concept behind blockchain is to create a tamper-proof system where data can be stored and verified without the need for a central authority.
Key Features and Benefits
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, allowing anyone to view the data.
- Security: Due to its decentralized nature and cryptographic algorithms, blockchain is highly secure and resistant to hacking.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring data integrity.
- Efficiency: Transactions can be processed faster and with lower fees compared to traditional systems.
How Blockchain Technology Works
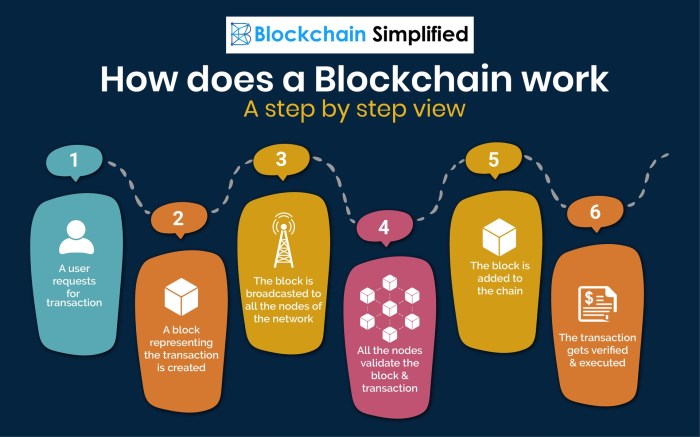
Blockchain works by creating blocks of data that are linked together in a chain. Each block contains a list of transactions along with a unique identifier called a hash. These blocks are then validated by network participants through a process known as consensus.
Types of Blockchain
In the world of blockchain technology, there are different types of blockchains that serve varying purposes and have distinct characteristics. Understanding the differences between public, private, and consortium blockchains, as well as permissioned and permissionless blockchains, is crucial to grasping the full scope of this innovative technology.
Public, Private, and Consortium Blockchains
Public blockchains are open to anyone and allow for transparent transactions without the need for permission to participate. They are decentralized and are most commonly associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. On the other hand, private blockchains are centralized and restrict access to certain participants who are granted permission. These blockchains are often used by organizations for internal purposes where privacy and control are key. Consortium blockchains fall somewhere in between, where a group of organizations work together to maintain the blockchain network. They offer a balance between decentralization and control, making them ideal for industries requiring collaboration.
Permissioned and Permissionless Blockchains
Permissioned blockchains require users to have explicit permission to participate in the network. This allows for greater control over who can access and validate transactions. On the other hand, permissionless blockchains are open to anyone who wants to join, providing a more inclusive and decentralized approach. Permissionless blockchains are commonly used in public networks, whereas permissioned blockchains are prevalent in private and consortium networks.
Comparison of Blockchain Networks
When comparing the various types of blockchain networks, it’s important to consider factors such as access control, decentralization, scalability, and privacy. Public blockchains offer high decentralization but may lack privacy, while private blockchains provide more control but sacrifice decentralization. Consortium blockchains strike a balance between the two, catering to specific industry needs. Understanding the nuances of each type of blockchain network is essential for choosing the right one for a particular use case.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has extended far beyond its original use case in cryptocurrencies. Various industries have started adopting blockchain to ensure secure transactions and streamline processes. Let’s explore some real-world applications of blockchain technology in different sectors.
Finance Industry
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the finance industry by providing a secure and transparent way to conduct transactions. Banks and financial institutions are using blockchain for cross-border payments, smart contracts, and digital identity verification. This technology has helped in reducing fraud, improving efficiency, and increasing trust among participants.
Healthcare Sector
In the healthcare sector, blockchain is being utilized to securely store and manage patient records. By implementing blockchain technology, medical professionals can access patient data quickly and securely, ensuring better coordination of care. Additionally, blockchain can help in tracking the authenticity of drugs and medical supplies, reducing counterfeiting and ensuring patient safety.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology is transforming the supply chain industry by providing end-to-end visibility and transparency. Companies can track the movement of goods from the manufacturer to the consumer in real-time, ensuring authenticity and reducing the risk of counterfeit products. Smart contracts on blockchain can automate processes like payments and inventory management, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps)

Smart contracts are self-executing contracts where the terms of the agreement between parties are directly written into lines of code. These contracts automatically execute and enforce themselves when predefined conditions are met, removing the need for intermediaries.
Decentralized Applications (DApps) are applications that run on a decentralized network of computers, such as a blockchain. DApps leverage blockchain technology to provide a secure and transparent way to interact with users while eliminating the need for centralized control.
Role of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts play a crucial role in blockchain technology by automating processes, reducing the risk of fraud, and increasing efficiency. They ensure trust between parties by executing transactions only when specific conditions are met, without the need for a trusted third party.
- Automate processes and transactions
- Reduce the risk of fraud
- Enhance efficiency and transparency
Benefits and Challenges of Smart Contracts and DApps, Blockchain technology
Smart contracts and DApps offer various benefits, such as increased security, reduced costs, and improved traceability. However, challenges like scalability, regulatory compliance, and code vulnerabilities need to be addressed for successful implementation.
- Benefits:
- Increased security
- Reduced costs
- Improved traceability
- Challenges:
- Scalability issues
- Regulatory compliance
- Code vulnerabilities