Running techniques are key to success on the track or trail. Get ready to dive into the world of proper form and efficient strides with a mix of style and substance.
From the importance of technique to biomechanics and training strategies, this guide will have you sprinting towards your running goals with confidence.
Understanding Running Techniques
Proper running techniques are crucial for preventing injuries and ensuring optimal performance. By maintaining good form, runners can reduce the risk of strains, sprains, and other common injuries that may result from poor technique. Additionally, efficient running techniques can help improve speed, endurance, and overall running efficiency.
Impact on Performance and Efficiency
- Improved Performance: Utilizing proper running techniques can lead to better performance outcomes, such as faster race times and increased endurance.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Efficient running form allows runners to conserve energy and maintain a steady pace throughout their runs.
- Reduced Risk of Injury: By avoiding overstriding, heel striking, and other common form mistakes, runners can minimize the likelihood of sustaining injuries.
Key Components of Good Running Form
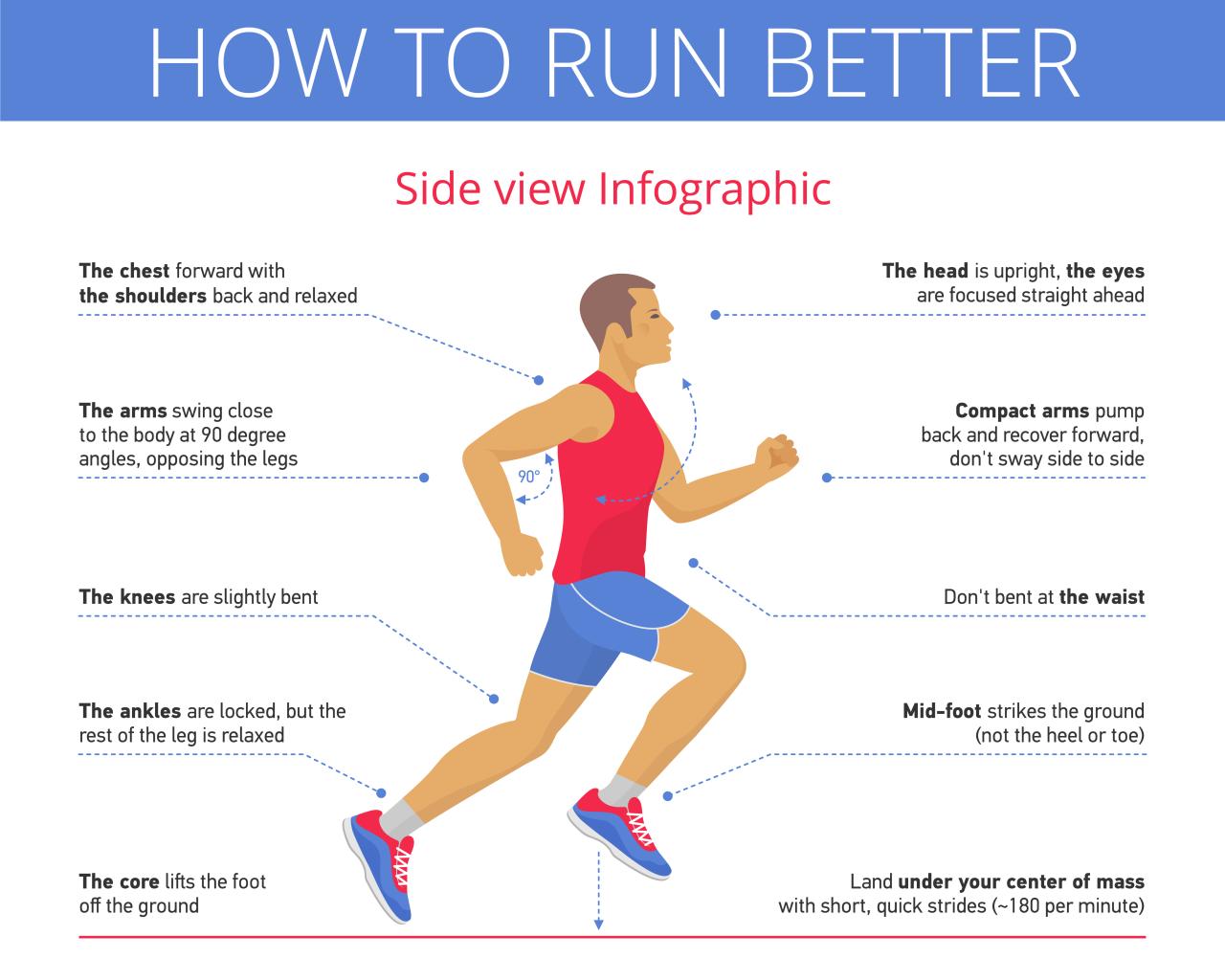
- Posture: Maintain an upright posture with a slight forward lean to promote efficient movement and reduce strain on the body.
- Footstrike: Aim to land midfoot to distribute impact forces evenly and avoid excessive stress on the joints.
- Cadence: Strive for a higher cadence (steps per minute) to improve running efficiency and reduce the risk of overstriding.
- Arm Swing: Keep your arms relaxed and bent at a 90-degree angle, swinging them back and forth in coordination with your stride.
- Breathing: Focus on deep, rhythmic breathing to supply your muscles with oxygen and maintain a steady pace.
Common Running Techniques
When it comes to running, there are several techniques that runners utilize to optimize their performance. Understanding the differences between forefoot striking, midfoot striking, and heel striking can help you determine which technique is best suited for your running style.
Forefoot Striking
Forefoot striking involves landing on the balls of your feet instead of your heels. This technique is often associated with a shorter stride length and a quicker cadence.
- Advantages: Helps reduce impact on joints, promotes better running posture, and can increase speed.
- Disadvantages: May put more strain on the calf muscles and Achilles tendon.
- Drills/Exercises: Practice running barefoot on grass to improve foot strike technique, perform calf raises to strengthen calf muscles.
Midfoot Striking
Midfoot striking involves landing on the middle part of your foot. This technique is often considered a balance between forefoot and heel striking.
- Advantages: Offers a balance between impact reduction and propulsion, can help with shock absorption.
- Disadvantages: May require more effort to maintain proper form and cadence.
- Drills/Exercises: Focus on landing softly on the middle part of your foot, practice running on different surfaces to adapt to varying terrain.
Heel Striking
Heel striking involves landing on your heels when your foot makes contact with the ground. This technique is commonly seen in beginner runners.
- Advantages: Offers stability and cushioning, requires less effort to maintain stride length.
- Disadvantages: Can lead to increased impact on joints and potential injuries, may slow down running speed.
- Drills/Exercises: Focus on landing with a midfoot strike and gradually transitioning to a forefoot strike, strengthen calf and shin muscles.
Biomechanics of Running: Running Techniques
When it comes to running, understanding the biomechanical principles is crucial for improving performance and preventing injuries. Let’s delve into how factors like stride length, cadence, foot strike, posture, and arm movement play a significant role in running mechanics.
Stride Length
Stride length refers to the distance covered by one step while running. It is essential to find the right balance, as an excessively long stride can lead to overstriding, causing inefficient movement and increased risk of injury. On the other hand, too short of a stride can result in a higher cadence and excessive energy expenditure.
Cadence, Running techniques
Cadence is the number of steps taken per minute while running. A higher cadence is generally associated with better running efficiency and reduced stress on the body. It is recommended to aim for a cadence of around 180 steps per minute to optimize performance and decrease the risk of overuse injuries.
Foot Strike
The foot strike pattern, whether landing on the heel, midfoot, or forefoot, can significantly impact running biomechanics. Proper foot strike can help in shock absorption, energy transfer, and propulsion. It is essential to find a foot strike pattern that works best for your body and running goals.
Posture and Arm Movement
Proper posture while running involves maintaining a straight back, relaxed shoulders, and engaged core muscles. Good posture not only improves breathing and running efficiency but also helps in preventing injuries. Additionally, arm movement plays a crucial role in balancing the body, generating momentum, and enhancing overall running mechanics.
Training Strategies for Improving Running Techniques
To improve your running techniques, it’s important to gradually transition to a new running style. This can help prevent injuries and allow your body to adapt slowly.
Role of Strength Training and Flexibility Exercises
Strength training plays a crucial role in enhancing running form by improving muscle strength and endurance. Focus on exercises that target the core, legs, and hips to build a strong foundation for better running techniques. Additionally, incorporating flexibility exercises such as yoga or stretching routines can help increase range of motion and reduce the risk of injuries.
Incorporating Drills and Intervals
Drills and intervals are effective ways to practice and refine your running techniques. Include drills like high knees, butt kicks, and strides to work on specific aspects of your form. Intervals, such as speed work or hill repeats, can help improve your speed and efficiency while running. By incorporating these training strategies into your routine, you can enhance your overall running performance and technique.

